How to Choose the Right Mobile App Database for Your Android and iOS Applications?
Mobile app development (for any platform) is a series of wise decisions and one such dilemma that is faced by many or almost all mobile app developers are picking the right core database to create an app or revamp an existing one.
Being in the business as a mobile app developer or a mobile app development company you can’t afford to lose your authenticity on the fact that your developed application is not performing well, is difficult to optimize, and is lacking speed. This is why the article is of utmost importance to you. Hopefully, by the end of this article, you will be confident with the database of your choice.
P.S. This article is an inspiration for the business that are looking to choose the right technology and resource for their business app. This will help you communicate well with your app-developing partner.
The Important Tags
The basis for Selecting the Right Database
-> General Considerations
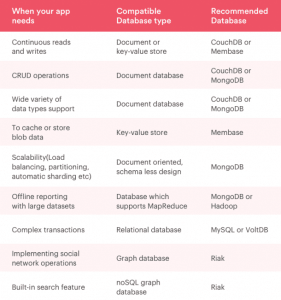
-> Based on the Use-Case
You Must Have Heard of these databases
4 Key Considerations While Working with Mobile App Databases
-> Predictive Caching
-> Filter your choices to Databases with MVCC
-> Keep in mind the Low Latency
The basis for Selecting the Right Database
Whether it’s Android, iOS App Development, hybrid, or cross-platform app development, choosing the correct database is the core need for any app developer. If you are regretting your past decisions, consider the following points as the basis for choosing the right database for your upcoming projects.
Basis of Database Selection – The Complete List
General Considerations
1. Data Storage
Your choice of database unapologetically depends on your data storage and access preferences. How do you want to store and retrieve your data? Some applications allow offline storing/access to the data while some restrict access to information only when the device has internet. Like e-commerce apps, lay on the second data storage and access model.
Apps that give access to offline information usually store the information in the receivers’ smartphones letting them have access as and when needed.
2. Data Size
As a mobile app developer, it is a wise choice for you to go for the databases keeping in mind the complexity and volume of the data that will be stored and accessed by the end consumer. The volume of data generally depends on the data structure and complexity of the mobile application you are aiming for. Various factors such as feature list, widgets, input, and navigational components, etc. coherently determine the size of your app data.
3. App Scaling and Speed
The scaling and speed of an application are directly concerned with the incoming reads and writes on the platforms. For instance, some interactive applications support heavy-writing while some are optimized to give heavy read benefits. How you want your app to handle the Input/Output of information can certainly be the base of your database selection.
4. Data Modeling
Data modeling is concerned with creating hierarchies of the data to be in an organized shell to represent its flow well.
Being an Android App developer or iOS App Developer, make sure you have done data modeling – representation of data structures that will be stored in the database. Data Modelling is not a privilege but a necessity for apps that have a number of search results, reporting, location-based features, and other such utilities.
5. Data Security Protocols
Data security becomes inevitable if you are working on an app that supports synchrony and decentralized storage of information. Secure access, storage, and transmission are a must. While you need authentication to allow users to access the app through standard, public, and custom authentication providers, there are certain apps for which you need to give anonymous access.
For moving data, communication should be established over a secure channel like SSL or TLS to maintain the integrity of the data (companies are required to mention it on their site/app). For an app’s read/write context, the database you choose should give limited control to the user for data access and modification.
6. Compatible With Multiple App Platforms
What’s your plan for app development in context to platforms – is that an Android-based app, iOS application, or both? What are your future integration plans with IoT or wearables? Being a mobile app developer, if you are planning to increase your reach to gadgets other than smartphones (IoT or wearables) then you might want to think about it at this moment.
If you are going for both Android and iOS app development then React Native is your go-to app development framework. The technology supports both the OS and it is easier to work simultaneously on apps for both the OS as the codes can be shared. Also, React Native supports all types of databases.
Based on the Use-Case
1. Data Synchrony between the database and local server
Modifications saved on the cloud
Several mobile applications proudly own features that can be accessed offline as well but these apps require a data connection to save the changes to the app’s local server. The changes you make offline will be directly synced to the cloud as soon as you have access to the internet connection.
As far as it is important, data synchronization is a complex process. Being a mobile app developer you have to think about various use-cases and accordingly choose the best database. Will your app be read-only or users are allowed to modify the existing data – like various social media apps or cloud worksheets. Go for a local database that gives automatic data synchrony/update to the cloud server and vice-versa as soon as the device has internet.
2. Synchrony between multiple layers of data
In-App Data Synchrony
Not only the external data synchronization but the in-app synchrony between the titles and segments of the app is a must. For instance, there is a field A that needs data synchronization with field B as changes in field A will directly affect the data in field B. under such circumstances it is recommended to go for unstructured databases rather than structured counterparts. Unstructured databases will help you introduce modifications without any pains that you might get while working with structured databases.
3. Optimized for people with low internet issues
Resolving Internet Deficiency
Generally, when an SQL database loses its connection from the client-side storage server, it shows an error despite transferring the data for the user’s convenience. If the problem is frequent then you might want to re-configure the database to a much reliable technology that can effectively resist the loss of internet connection.
4. High Scalability
When it comes to application with scalability means you are increasing the premises of the app functionalities by adding more resources in the form of servers, making the database more efficient and client-centric. The database you pick should be capable enough to utilize the resources and in-lieu handle parallel data processing. In short, the process needs a multi-threaded database.
Multithreading lets the database support parallel processing minimizing the workload on the local server. Not limited to multi-threading but a distributed design of the database also contributes significantly to the scalability of an app.
Being a mobile app developer you must know, distributed designed database comes at your greatest advantage by letting you split the services so that there is no overload on the main app database.
5. App Updates and database changes
A mobile app update brings changes to its local database. This is an important scenario to look at and it is equally difficult for the mobile app developers working on the updates. With the updated version you have to keep the old version too of the database.
The database you pick for mobile app development should be able to incorporate new fields and tables as well as manage the old APIs with the database structure. Go for SQLite for the server-side database.
6. Resolving the Data Cacophony between devices
A mobile app development company or a mobile app developer is well-versed with the common problem of data conflict – modifying the same data on various devices might create conflicts. The database should be potent enough to automatically resolve the conflicts on the device, in the cloud, by an external system, and by a human.
(source: simform)
You Must Have Heard of these databases
The database is a structured/unstructured set that controls the functionalities on Android and iOS apps, it is incredibly important to know which one you are working with in order to get the best mobile application. Being a mobile app developer, the database can be your biggest asset or a hurdle, lets see some assets that you can use in mobile application development:
| MySQL | Open source, multi-threaded, and easy to use. |
| PostgreSQL | Much powerful open-source relational database, highly customizable. |
| Redis | Open-source, value store for data caching, low maintenance database. |
| MongoDB | JSON-based database, flexible, scalable and has no schema. |
| Memcached | A distributed cache system, used to cache the system to enhance application speed, helps in easing database load. |
| MariaDB | An open-source database, relational and created by the developers of MySQL. |
| Cassandra | An open-source network, no SQL database, used to manage loads of unstructured data, free-of-cost. |
| SQLite | Embedded database, used to give local storage space to the device for storing data. |
| InfluxDB | Open-source set written in Go, a fast and time-series database. |
| RethinkDB | RethinkDB stores data in a JSON format, open-source, document-oriented database that syncs in real-time with the application. |
| Riak DB | Distributed NoSQL database with features such as fault tolerance, resiliency, and high availability. |
| CouchDB | NoSQL document-based database that uses JSON as a data storage medium and Javascript as its key query language. |
| Couchbase | NoSQL database to support offline sync of application data, full CRUD and query capabilities, runs on the device with the application installed. |
| ArangoDB | An open-source database, NoSQL, is known for its multi-model features, graph and geo algorithms. |
Explore: Top 10 Platform As A Service (PaaS) Providers for business needs in 2021
4 Key Considerations While Working with Mobile App Databases
Getting your hands on just the database is as challenging as it is important, here are some best practices for working with the database. This applies to mobile app developers and app development companies too.
1. Predictive Caching
Concerned with improving the performance of the business mobile application, Predictive Caching helps the backend to know that when, where, and how your application is being used by the end-consumer.
With such information in hand, user behavior can be tested giving them more apt information that piques their interests and increases the clicks. The data is made available even before the user logs in to the application. Just like MongoDB – the database works on predictive caching to provide the reliable and most apt information to the clients.
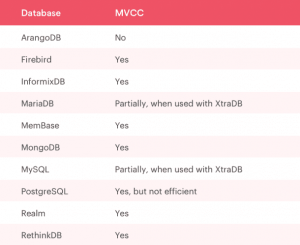
2. Filter your choices to Databases with MVCC
Multi-Version Concurrency Control or MVCC supports simultaneous access without blocking the threads or processes involved. The capability allows the reader to view a snapshot of the data before the writer changes the information, supporting parallel read and write options.
Here is the table to show which popular databases have MVCC and which lack the utility:
(source: simform)
3. Keep in mind the Low Latency
Whether you are an Android App Developer or an iOS App Developer you cannot (at any cost) avoid the issue of high latency. Especially for real-time and gaming apps, the high latency issue is a dead end. Anything that goes below 500ms is said to be high latency.
Latency optimization is a constant process and each database has its own limits as to what extent it can be optimized or replicated.
Here are some examples of low latency databases:
-> MongoDB
-> RethinkSQL for real-time app
-> PostgreSQL for real-time and transactional apps.
-> PipelineDB, SQL database for video streaming applications.
The right choice in databases is not enough, know the top 14 Python Frameworks you can use for web and mobile app development in 2021.
4. Caching Databases to reduce the load on servers
Caching layer to the database is used to reduce the data load on the servers by preventing the recurring requests for the same data to go to the server. This ultimately lessens the load of requests on the servers making them work more proficiently.
Know 15 best Magento Website Examples for E-Commerce Business
For instance, an e-commerce portal like Amazon gets a lot of recurring requests that can be store in the caching layer of its database and ultimately reduce the load on the server. The portal is capable enough of handling the recurring requests with the lowest latency. To develop such an application, Redis and Memcached can be used.
Conclusion
Application databases that you are using have a lot to do with your reputation as a mobile app developer or a mobile app development company. And with today’s apps being more flexible and scalable in terms of features, improvement, and functionality, you have to determine that the database you are using should be highly flexible and support low latency.
As an accomplished business mobile app development company, we can say that the true basis for judgment on databases should be flexibility, scalability, and low latency with cached layers to reduce the load on the main server.